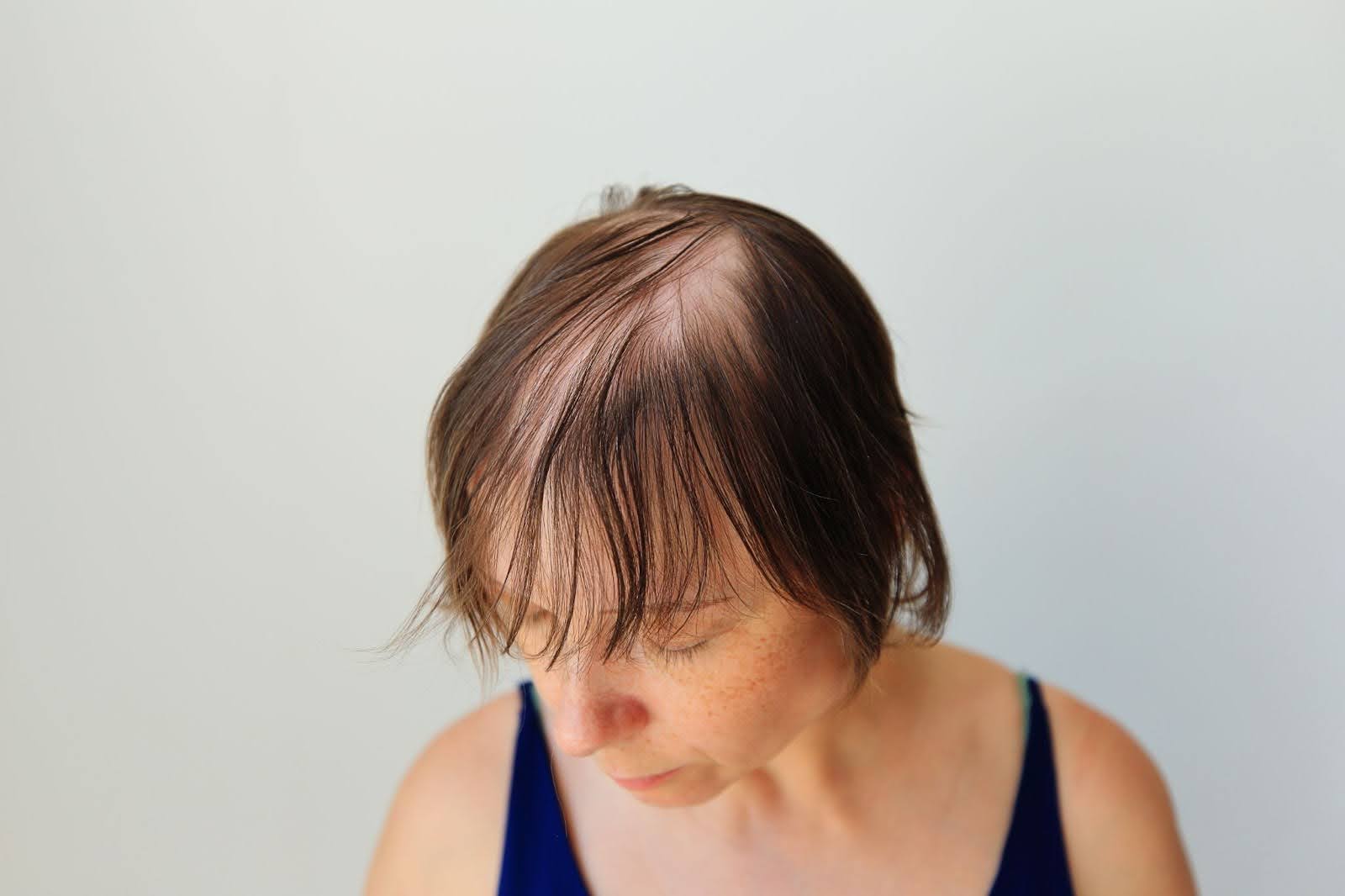
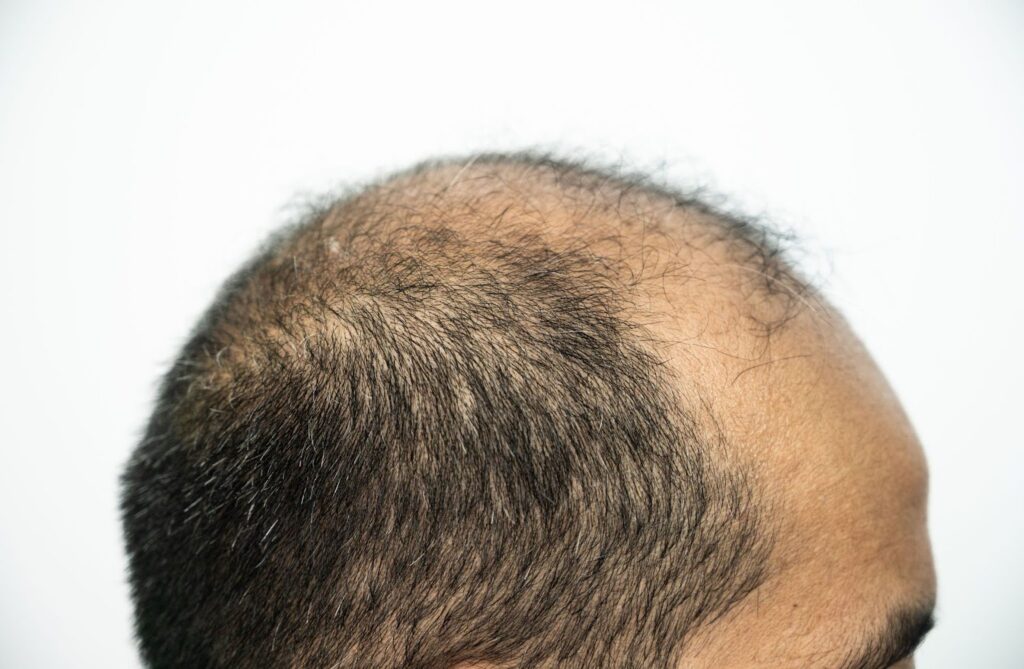
Hair loss is incredibly common; in fact, statistics show that many men and women will experience some level of thinning hair at some point during their life. But if hair loss itself is quite common, its causes are myriad. There are any number of factors that may contribute to a thinning head of hair.
Determining the underlying cause of your hair loss may provide some clues as to how to address it. In some cases, simple lifestyle changes may help reduce thinning hair. In many other instances, medical intervention, including surgical hair transplants, are required to restore full coverage.
What Causes Hair Loss?
With that in mind, let’s take a closer look at some of the most common causes of male and female hair loss.
1) Androgenetic alopecia
You may not be familiar with the term androgenetic alopecia, but you are surely familiar with its more common nicknames: Male pattern hair loss or female pattern hair loss.
Whatever you want to call it, this is by far the most common cause of hair loss among men and women alike. This is a genetic condition that can begin to manifest during puberty, though the results usually do not become particularly noticeable until later in life.
Note that androgenetic alopecia is linked with hormone cycles, so for many women it begins in earnest during menopause.
2) Pregnancy
Speaking of hormone-related hair loss, many women shed a lot of hair during pregnancy. This is a result of decreased estrogen production. The good news about his type of hair loss is that it is usually temporary, and much of the time it clears up within a year after giving birth.
3) Telogen effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a medical condition that may result in either temporary or long-lasting hair loss.
Hair loss happens in four distinct phases, including one phase (the telogen phase) in which your follicles shed old hairs to make room for new, healthy growth. This shedding is normal and natural, but telogen effluvium extends this phase, meaning you continue to lose hair without new hair growing in to replace it.
This condition is typically exacerbated by pregnancy, surgery, significant weight loss, or conditions of the thyroid.
4) Anagen effluvium
Here is another medical condition that alters the typical hair growth cycle… only in this case, it results in hair falling out of the follicles during the anagen phase, which is normally when new growth occurs.
This condition is typically caused by an autoimmune disorder or by certain cancer treatments, including chemotherapy and radiation treatments.
5) Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder, one in which your body attacks the hair follicles as if they are foreign invaders.
Because your immune system attacks the follicles indiscriminately, it can result in hair loss not just on your scalp but elsewhere on your body, such as the eyebrows.
This condition is usually characterized by patchy or clumpy hair loss and is typically very treatable with pharmaceutical interventions.
6) Traction alopecia
This form of hair loss is linked with lifestyle factors. Specifically, traction alopecia occurs when you regularly wear hairstyles that pull the hair tight, causing it to break and come loose. Traction alopecia can ultimately scar your follicles, which might make the condition permanent.
Traction alopecia may result from hairstyles including braids, tight buns and ponies, or cornrows. Getting hair extensions may also result in traction alopecia.
The good news about traction alopecia is that, simply by avoiding certain hairstyles (or by using them sporadically), you can usually steer clear of this condition.
7) Medications
There are a number of common pharmaceutical interventions that list hair loss among their chief side effects. Some examples include:
- Acne treatments
- Antifungal medications
- Antidepressants
- Beta-blockers
- Drugs to lower cholesterol
- Drugs to treat thyroid conditions
- Drugs made with hormones
If you are taking any of these medications and experience the symptoms of hair loss, ask your doctor if there are any alternative treatments available.
8) Birth control
Speaking of medications, the birth control pill can also be a major contributor to hair loss. In fact, birth control treatments can cause hair loss immediately, or a delayed effect several weeks or months later.
If you are taking birth control and notice your hair starting to shed, ask your doctor for alternatives. Usually, switching to a birth control with a low androgen index can help prevent the symptoms of hair loss.
9) Ringworm
Believe it or not, the fungal infection known as ringworm can also be a culprit when it comes to hair loss. Specifically, ringworm can lead to temporary patches or hair loss along the scalp.
Ringworm may result in other symptoms, as well, which can include:
- Itchiness all across your scalp.
- Oozing blisters.
- Scaly or discolored patches on your skin.
Thankfully, medication is usually sufficient for clearing up ringworm, assuming it does not heal all on its own.
10) Poor nutrition
A final factor that can contribute to hair loss is nutritional deficiency.
Specifically, you may experience hair loss if your diet is too low in protein, or if you fail to get enough iron.
Talking with a doctor about ways to alter your nutritional habits can usually correct this issue promptly.
No Matter the Cause of Your Hair Loss, There is Always a Solution
The bottom line: No matter the cause and no matter the extent of your hair loss, there are always ways to address it. In many cases, a NeoGraft hair transplant is the best option to restore you to a full head of healthy, natural hair.
Learn more about the different approaches to hair restoration and confirm your eligibility for NeoGraft treatment. Reach out to the team at Renu whenever you’re ready to schedule a consultation.